Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 10 (6); November 25, 2020![]() [Booklet]
[Booklet]
Recent drugs and vaccine candidates to tackle COVID-19
| Recent drugs and vaccine candidates to tackle COVID-19 |
Gharib Mombeni E, Yousefi M, Chekani-Azar S, Abousenna MS, Armin K, Shavandi F, Emami E and Bahrami Y.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 10(6): 70-79, 2020; pii:S225199392000009-10
![]() DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51145/jlsb.2020.9
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51145/jlsb.2020.9
Abstract
Introduction. The global devastating pandemic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a worldwide multisystemic infection caused by the novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which has emerged as a menace to the global public health and countries economy. There is a crucial necessity for the suggestion of effective drugs to eliminate the virus outbreak. Several candidate drugs with existing emerging evidence try to offer a pharmacological strategy that may inhibit infection in COVID-19 patients. By, October 2020, scientists have nominated some reliable and safe types of coronavirus vaccines like Pfizer, Moderna, AstraZeneca, CureVac, CoronaVac, etc. that are effective and showed 95% to 90% protection, respectively. Aim. This review highlights important clinical and in vitro studies, uses of potent antiviral drugs and most recent vaccines against COVID-19 disease.
Keywords: Actemra, Antiviral medicines, ARCoV, AstraZeneca, ChulaCov19, CoronaVac, COVID-19, CureVac, CytoSorb, Ivermectin, Moderna, Oleandrin, Pfizer, Remdesivir, Ritonavir, Vaccines.
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [ePub] [XML] [Export citation to BibTeX, RIS & EndNote] [How to Cite] [Google Scholar] [Dimensions ID]
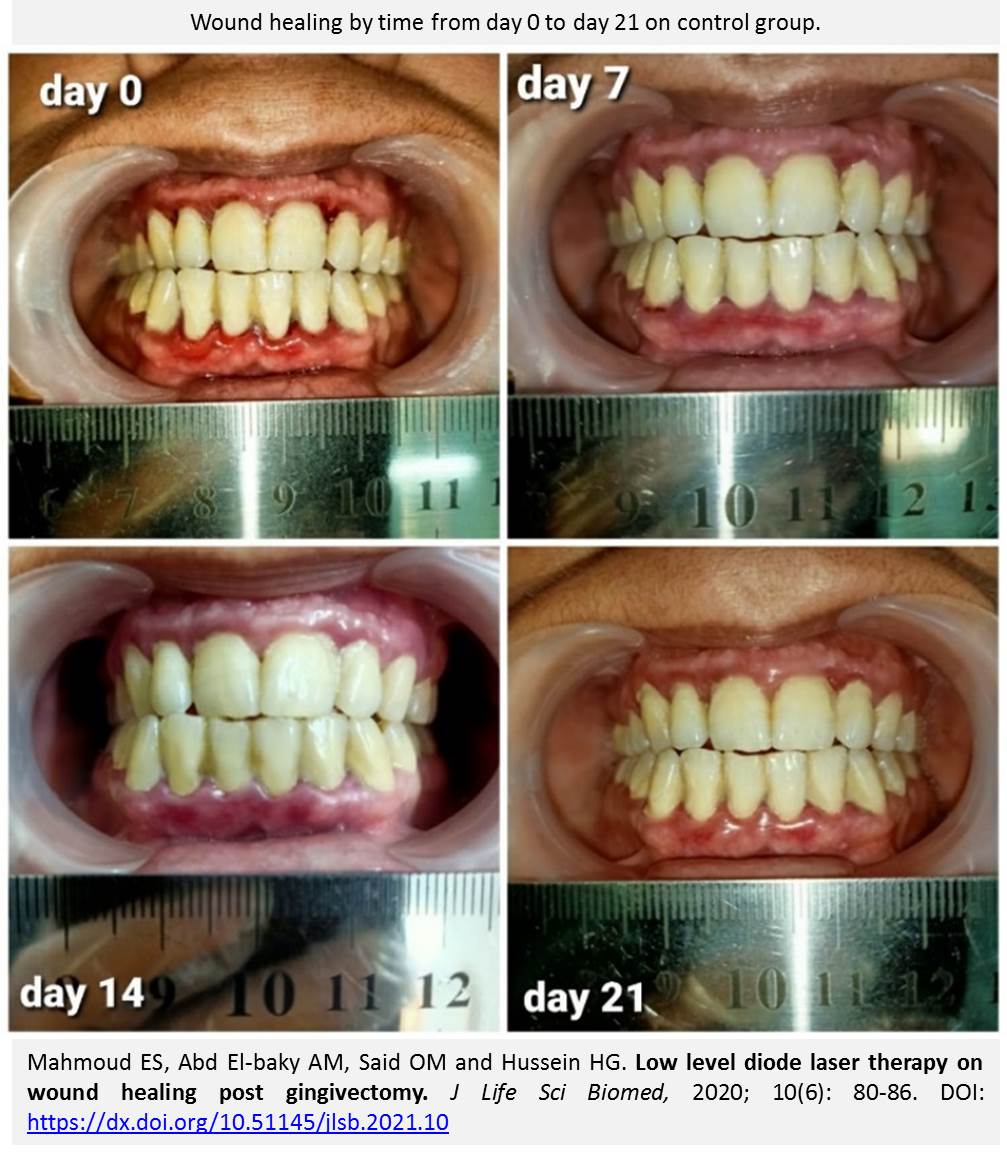
Low level diode laser therapy on wound healing post gingivectomy
| Low level diode laser therapy on wound healing post gingivectomy |
Mahmoud ES, Abd El-baky AM, Said OM and Hussein HG.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 10(6): 80-86, 2020; pii:S225199392000010-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51145/jlsb.2020.10
Abstract
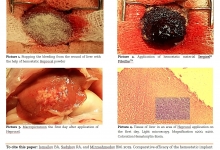
Aim. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of low-level diode laser therapy on wound healing after gingivectomy. Methods. Forty patients (male and female) with ages ranged from 20-40 years, and who received gingivectomy were participated in this study. They were selected randomly from dental outpatient clinic at Badr university in Cairo and randomly divided into two equal groups, including the study group (A) and control group (B). The study group (A) was irradiated with Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) laser of wavelength 850 nm for 4 sessions on day 0, 3, 7 and day 14 post gingivectomy, while the control group (B) received placebo laser. Assessment of healing was done before starting the first session (day 0), after session (days 7 and 14) and follow up on day 21. The healing assessed by Landry index. Results. The results of this study supported that the low-level diode laser therapy was significantly effective (p < 0.001) on wound healing in patients after gingivectomy. Conclusion. It was concluded that the low-level diode laser therapy is an effective method for increasing wound healing after gingivectomy.
Keywords: Low level diode laser therapy, Wound healing, Gingivectomy
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [ePub] [XML] [Export citation to BibTeX, RIS & EndNote] [How to Cite] [Semantic Scholar] [Dimensions ID]