Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() Volume 12 (5); September 25, 2022
Volume 12 (5); September 25, 2022
| Outcomes of pregnant women with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) admitted to intensive care unit in Uzbekistan |
Research PaperCOVID-19
Outcomes of pregnant women with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) admitted to intensive care unit in Uzbekistan
Ibadov RA, Alimova KhP, and Voitova GA.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 12(5): 82-88, 2022; pii:S225199392200010-12
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2022.10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2022.10
Abstract
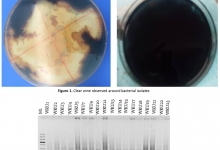
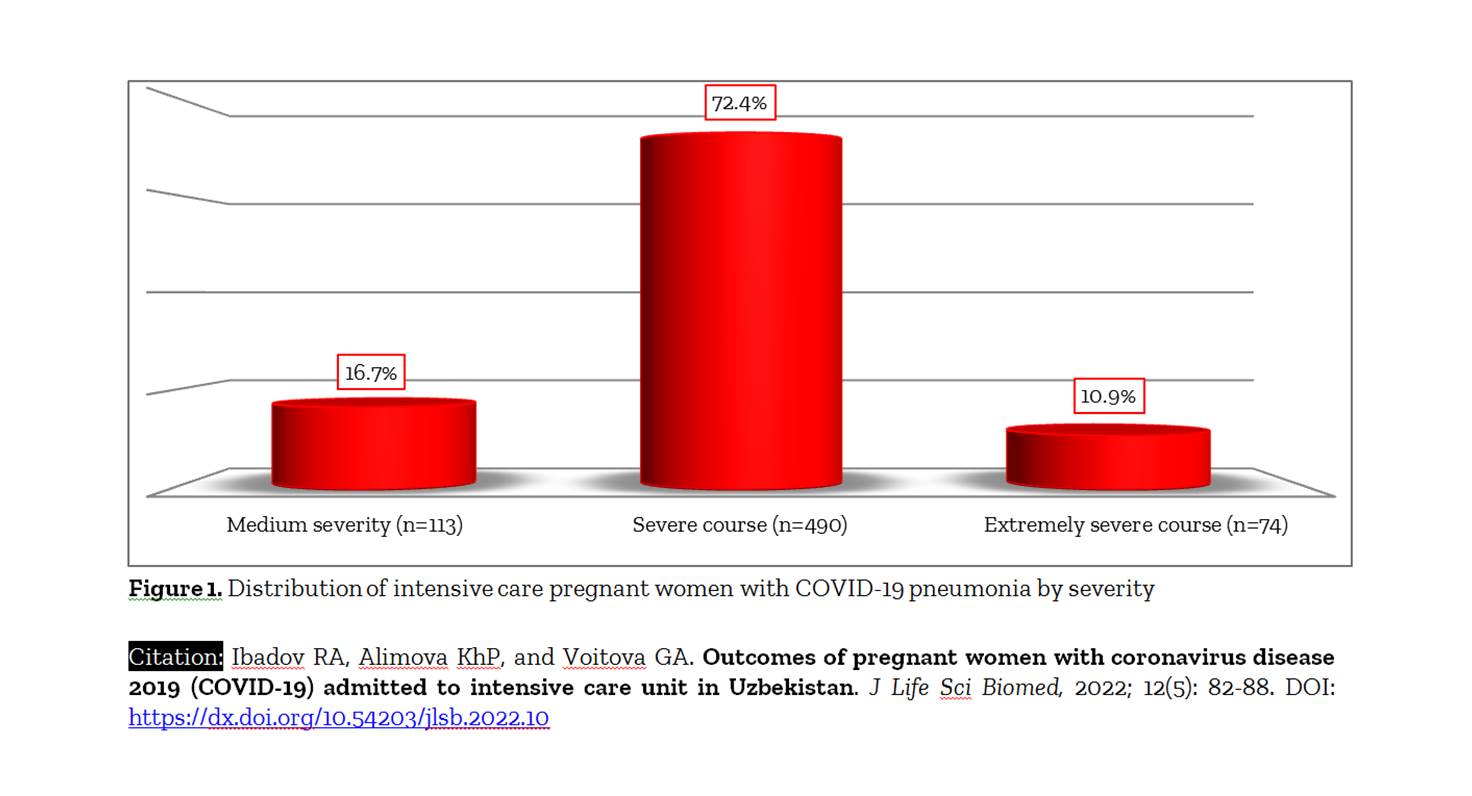
Aim. The present study aimed to investigate outcomes of pregnant women with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2 or COVID-19) in the intensive care unit (ICU). Methods. A total of 3080 pregnant women infected with COVID-19 during treatment were studied in the maternity ward of the Zangiota-1 Republican Specialized Infectious Diseases Hospital from December 2020 to January, 2022. At the time of admission of patients to the hospital, 28.9% of women were in the first trimester of pregnancy, 34.3% and 36.8% were in the second and third trimester of pregnancy, respectively. 1980 cases (64.3%) showed a moderate course of pneumonia and in 48% (1478 cases), bilateral pneumonia was detected. At the same time, 60.0% of patients had lung damage (up to 50%) according to CT dataset. Results. A total of 677 out of 3080 pregnant women with COVID-19 pneumonia (22.0%) needed treatment at the ICU. 490 cases out of 677 patients showed severe clinical course of COVID-19, while 277 cases (41%) showed multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS). Of 277 MODS cases, 209 (75.4%) were those in the third trimester of pregnancy and 170 (61.4%) had initially severe clinical picture of COVID-19. Mortality rate in ICU was 9.4% (64 cases out of 677) while 56.6% experienced post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) at baseline, 26.7% had general anxiety disorders, and 16.7% (113 of 677) of women experienced depression symptoms. In the postpartum period, 46.1% (312 of 677) cases showed combinations of PTSD, anxiety and depression according to the combined Patient Health Questionnaire Anxiety and Depression Scale (PHQ-ADS) assessment, which was typical for women with severe and extremely severe COVID-19, preterm birth, miscarriages and perinatal mortality. Conclusion. The ICU hospitalization rate for COVID-19 pneumonia in pregnant women was 22.0%, among which the vast majority (72.4%) were cases with severe clinical course of COVID-19 and PTSD (56.6%). Women in the third trimester of pregnancy were most susceptible to developing MODS and severe COVID-19 pneumonia. Recommendation. In promoting pregnant women's mental and physical health, understanding the characteristics of psycho-emotional stress disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic and learning how to deal with them is critical.
Keywords: COVID-19 pneumonia, Intensive care unit, Mental and physical health, Pregnant women
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
| The quality of life of lumbar compression radiculopathy patients under microsurgical treatment |
Research Paper
The quality of life of lumbar compression radiculopathy patients under microsurgical treatment
Karimov AA and Akhmedzhanov DU.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 12(5): 89-96, 2022; pii:S225199392200011-12
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2022.11
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2022.11
Abstract
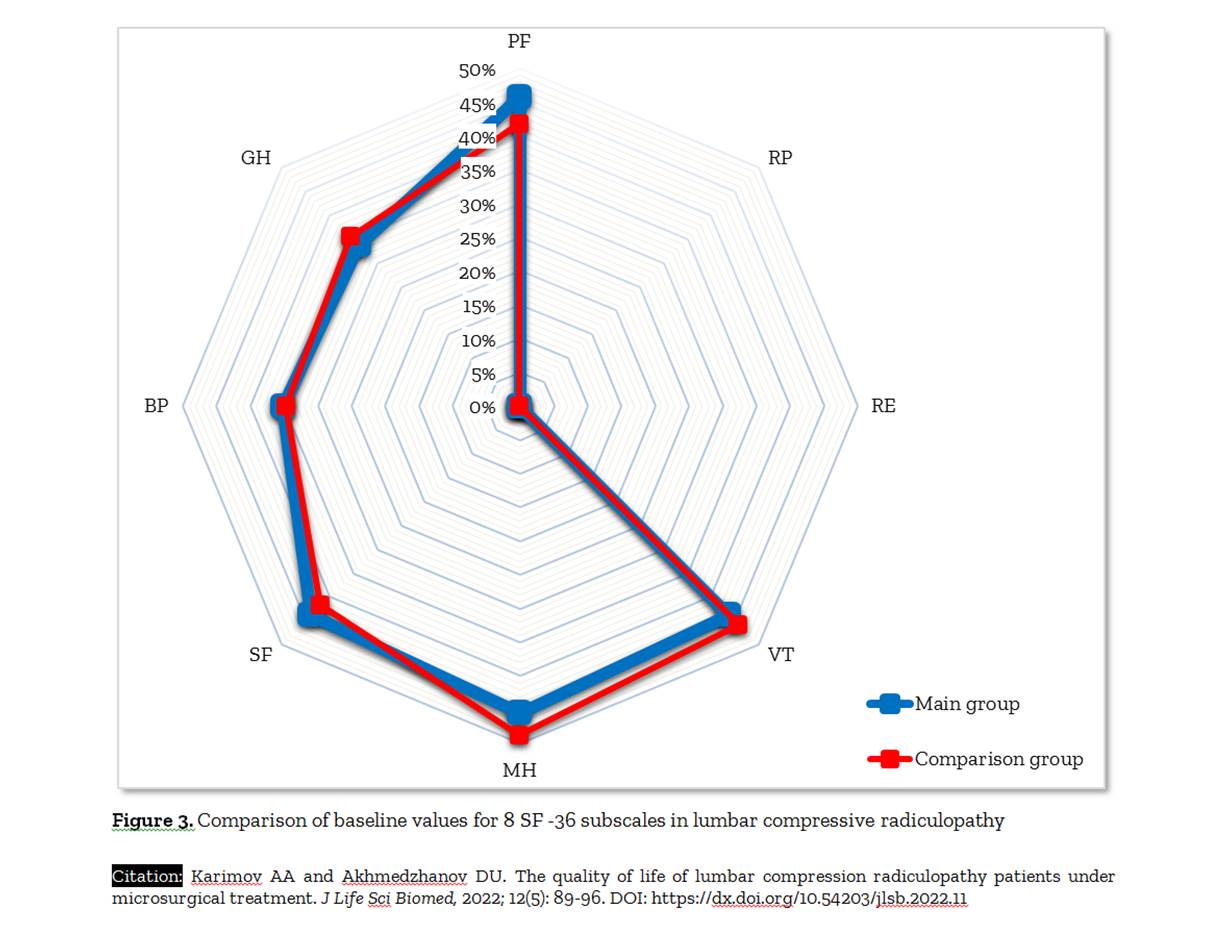
Aim. The present study aimed to conduct a prospective comparative analysis of the quality of life of patients up to 12 months after microsurgical treatment of lumbar compressive radiculopathy. Methods. A prospective study involving 120 patients with lumbar compressive radiculopathy operated on at the State Institution "Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Endocrinology named after Academician Y.Kh. Turakulov" from January 5, 2020 to November 2021. The main group included 60 patients (32 men, 28 women, with mean age of 43.2 years). The comparison group also included 60 patients (34 men and 26 women, with mean age of 45.9 years). In the main group, the tubular technique was used, and in the comparison group, the Caspar microsurgical discectomy method. The Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) ranged from 30% to 98%. Quality of life was assessed using the 36-item short form (SF-36) health survey at 3, 6 and 12 months. Results. The vast majority of patients, (87.5% of the main group and 71.1% of the comparison group) had no restrictions (χ 2=4.509; df=1; p=0.034). In the main group of patients, physical well-being was increased from the initial 32 to 56 points, and mental well-being increased from 43 to 57 points, while in the comparison group these indicators were significantly lower and amounted to 46.7 and 48.4 points. In the immediate period after the operation, significant differences (p<0.05) were obtained in terms of physical (34.2±8.2 vs. 29.5±5.2), role functioning and social functioning (58.6±7.8 vs. 51.2±8.8) and vital activity (56.1±6.3 vs. 49.9±8.0). After 12 months, the differences were also statistically significant and the average quality of life score was 82.6 points in the main group and 78.6 points in the comparison group. Conclusion. The tubular technique of microsurgical treatment of lumbar compressive radiculopathy is characterized by a faster recovery of the patient's functional status, a low recurrence rate of pain and radicular syndromes, and better indicators of quality of life.
Keywords: Lumbar compressive Radiculopathy, Microsurgical treatment, Postoperative period, Quality of life
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0)
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0)