Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 9 (6); November 25, 2019 [Booklet]![]()
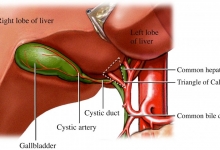
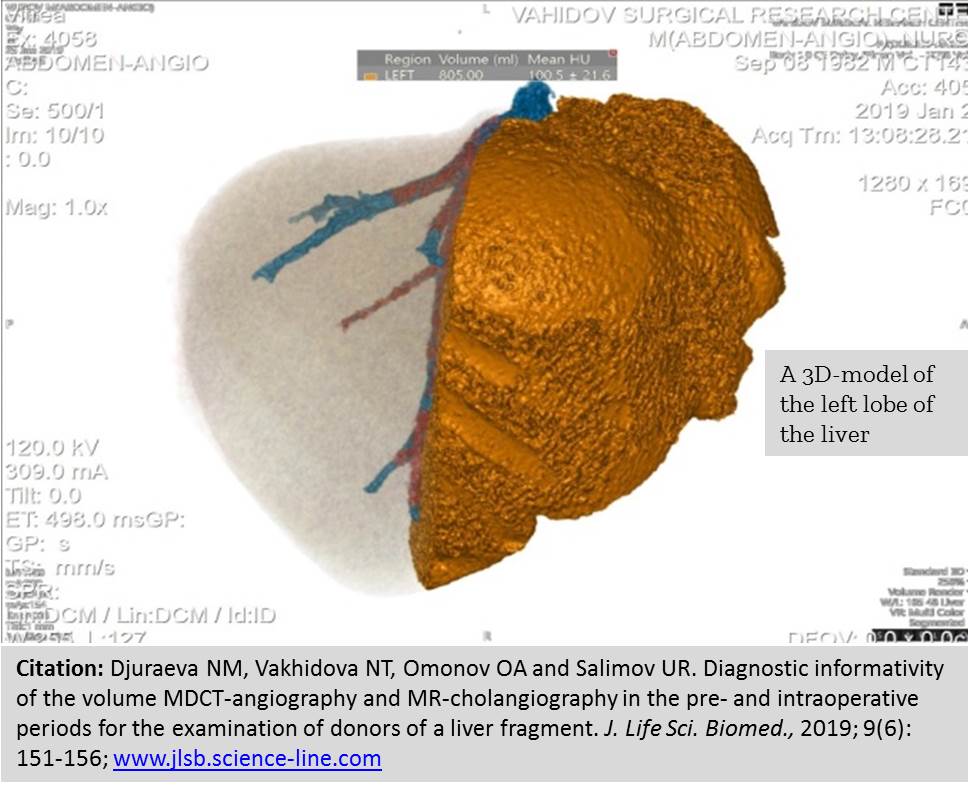
Diagnostic informativity of the volume MDCT-angiography and MR-cholangiography in the pre- and intraoperative periods for the examination of donors of a liver fragment.
Nazirov FG, Djuraeva NM, Vakhidova NT, Omonov OA and Salimov UR.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(6): 151-156, 2019; pii:S225199391900024-9
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2019.jlsb24
Abstract
Introduction. The first transplantation of a liver fragment from a living donor was performed in Uzbekistan on February 12, 2018 at the Republican Specialized Scientific Practical Medical Center of Surgery named after acad.V. Vakhidov. This event laid the foundation for a new direction for domestic clinical practice that meets the current level of world medicine development. Aim. The aim of the study was to determine the diagnostic information content of preoperative data of the volume multi detector computed tomography (MDCT) angiography and magnetic resonance cholangiography (MRCG) when compared with intraoperative ones at examining related donors for liver fragment transplantation (LFT). Methods. Total of 88 potential donors of a liver fragment aged from 19 to 58 years (53 men and 35 women) were examined for the period 2017-2019. Sixteen donors were undergone liver resection to obtain a transplant: the right lobe of the livers in 12 people and the left lobe in 4 people. Results. Compared with intraoperative data, the main arteries supplying the transplant planned for resection were identified with MDCT-angiography in 98.4% of cases (P<0.05). Variations of the portal bed according to MDCT-angiography in comparison with intraoperative ones were determined in 93.8% of cases (P<0.05). Intraoperatively revealed the main trunks of the venous outflow were determined by MDCT-angiography in 95.7% of cases (P<0.05). Recommendation. We suggest that MDCT angiography and MRCG is a highly informative and important method for estimation the condition of the liver in transplant planning.
Keywords: Liver transplant, Contrast agent, MDCT-angiography, Magnetic resonance cholangiography.
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
Genetically modified foods (GMOs); a review of genetic engineering.
Gatew H and Mengistu K.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(6): 157-163, 2019; pii:S225199391900025-9
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2019.jlsb25
Abstract
Aim. This review article mainly focuses on the importance, possible risks and state of public debate on genetic engineering particularly on genetically modified organisms (GMOs). During the last decade, tremendous progress has been made in the area of genetic engineering. The technology has numerous applications in increasing productivity of agriculture (in farm animal and plant species) and biomedical industries. Creation of resistant varieties of plants, transgenic animals, increasing the protein content, bio-fertilization, recombinant pharmaceuticals and gene therapy are now the major application of genetic engineering. Despite the technology has opened up new opportunities for highly specific manipulation of the genetic material of organisms, it has the possible risks of genetic contamination/inbreeding, competition with natural species, ecosystem damage, risk of horizontal gene transfer, new kinds of outbreak diseases; creation of drug resistant germs; accidental escape of laboratory strains and increased disease burden if the recipient organism is a pathogenic microorganism or virus. Additionally, now, scientists are faced with ethical issue challenges related to moral and religious acceptance and animal welfare. Conclusion. Scientists need to consider the types of applications of genetic engineering which will appear on the commercial market as well as develop procedures which will minimize potential biological and ecological hazards of the technology. Even though, genetically modified foods currently available on the international market have passed safety assessments, countries vary in their regulation of genetically modified foods indicating the necessity of worldwide consensus on labelling and traceability of genetically modified foods taking into account health and environmental risks as well as religious issues.
Keywords: Preterm Acceptance, Benefits, Biological and ecological hazards, Ethics, Farm animal, Genetically modified organisms (GMOs), Human health, Plant
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
In vitro nematicidal activity of Juglone against Meloidogyne incognita race 2 infesting pomegranate.
Laxmikant D.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(6): 164-169, 2019; pii:S225199391900026-9
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2019.jlsb26
Abstract
Introduction. Juglans regia L. (walnut) is also known as the medicinal plant and native to the mountain ranges of central Asia. Recently, a severe infestation of root-knot nematodes (RKN, identified as Meloidogyne incognita race 2), was observed on Punica granatum L. (pomegranate). Aim. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of in-vitro nematicidal activity of the purified bioactive compounds (Juglone: 5-Hydroxy 1, 4-Napthoquinone) isolated from medicinal plant like walnut on Meloidogyne species associated with pomegranate under field conditions. Methods. Plants are cultivated at the agricultural farm in Solapur, (M.S.), India. Results. Roots of infected plants were heavily galled and soil samples collected from the affected plants second stage juveniles (J2). The ability of treatment schedule of Juglone was tested using an in-vitro method against RKN - Meloidogyne incognita race 2 infesting pomegranate. Juveniles in the control (distilled water; carbofuran) were compared with treated groups. The Juglone showed a 100% mortality in 5 µl/ 10 ml of distilled water/ 100 nematodes.
Keywords: 5-Hydroxy 1, 4-Napthoquinone, Nematicidal activity, Root-knot nematode, Punica granatum L.
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
Ethnogeographic features of nutrition as a key factor in the development of iron deficiency anemia in the Bukhara region.
Akhmedova DR.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(6): 170-173, 2019; pii:S225199391900027-9
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2019.jlsb27
Abstract
Introduction. Ecological disasters, industrial pollution, and poor nutrition lead to significant changes in the content of microelements (MEs) in food and, as a consequence, in the human body, while toxic MEs accumulate, displacing essential ones. Iron deficiency anemia refers to biogeochemical poly-microelementosis. For the prevention and treatment of iron deficiency anemia (IDA), drugs containing microelements are used along with traditional methods of treatment. Aim. This study aimed to investigate the nutritional characteristics and the ME content in the diet in order to clarify the etiology of IDA, the role of microelementosis in its development, and to also identify indicators of red blood parameters in families living in the Qorovulbozor district of the Bukhara region. Methods. Ten families were examined, each consisting of a husband, a wife, and female children. In order to facilitate the analysis of the results obtained, the husbands and wives selected for examination from those were aged between 30 and 45 with daughters from 12-17 years old. The content of MEs in erythrocytes and blood serum, in tap water, and in irrigation ditch (arch) water was determined. Results. A relatively favorable picture was observed only in men, while 1-3 degree IDA was observed with almost the same frequency in both mothers (75-78.5%) and their daughters (20-21.4%), respectively. Daily nutrition was roughly estimated by dividing the volume of food consumed per week into 7 days and the number of family members. Despite this, iron deficiency turned out to be significant for such products as meat, milk, bread, eggs, and fruit. This served as the basis for convincing the subjects of the need for proper nutrition and the administration of ME containing preparations (Vitrum Prenatal Forte). Conclusion. In order to exclude the entry of toxic MEs into the body, it is advisable to use mineral water for food, especially during pregnancy, instead of tap water. Our findings provide the basis for the need to correct the ME composition of the body with the necessary MEs, not only by increasing the volume and quality of food products, but also by using medications containing MEs.
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Semantic Scholar]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 9 (4); July 25, 2019 [Booklet]![]()
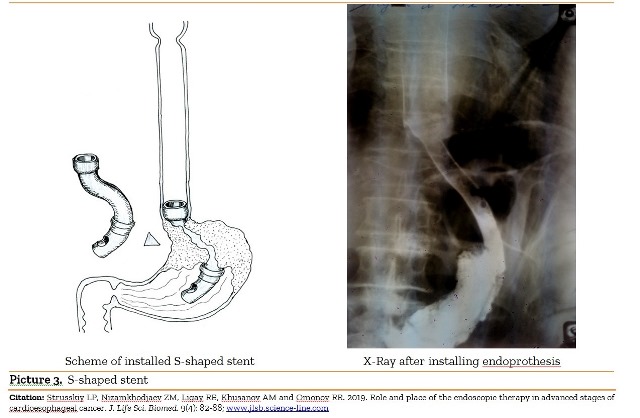
Role and place of the endoscopic therapy in advanced stages of cardioesophageal cancer.
Strusskiy LP, Nizamkhodjaev ZM, Ligay RE, Khusanov AM and Omonov RR.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(4): 82-88, 2019; pii:S225199391900013-9
Abstract
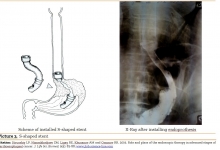
Aim. The aim of study was to investigate efficacy of palliative treatment of proximal gastric tumors. Methods. The article describes experience of treating 232 patients with unresectable cardioesophageal cancer (UCC). Of these, minimally invasive endoscopic procedures: endoscopic diatermotunnelization (ED), endoscopic bougienage (EB) and endoscopic stenting (ES) was performed in 101 patients. Currently, the method of endoscopic stenting is preferred, which was performed in 84 patients, and own-developed model of a silicone tube stent was used in all patients. Main early and late complications of using this method were described. Results. Minimally invasive techniques described, the absence of a cosmetic defect, there is no need of specific care set endoprothesis and relatively easily tolerated by patients of the technique endoprosthetic stent installation suggest a viable alternative to the imposition of gastrostomy and jejunostomy.
Keywords: Tumours of the proximal part of the stomach, Surgical treatment, Unresectability, Invasive technologies, Diathermotunnelization, Endoscopic bougienage, Endoscopic stenting.
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
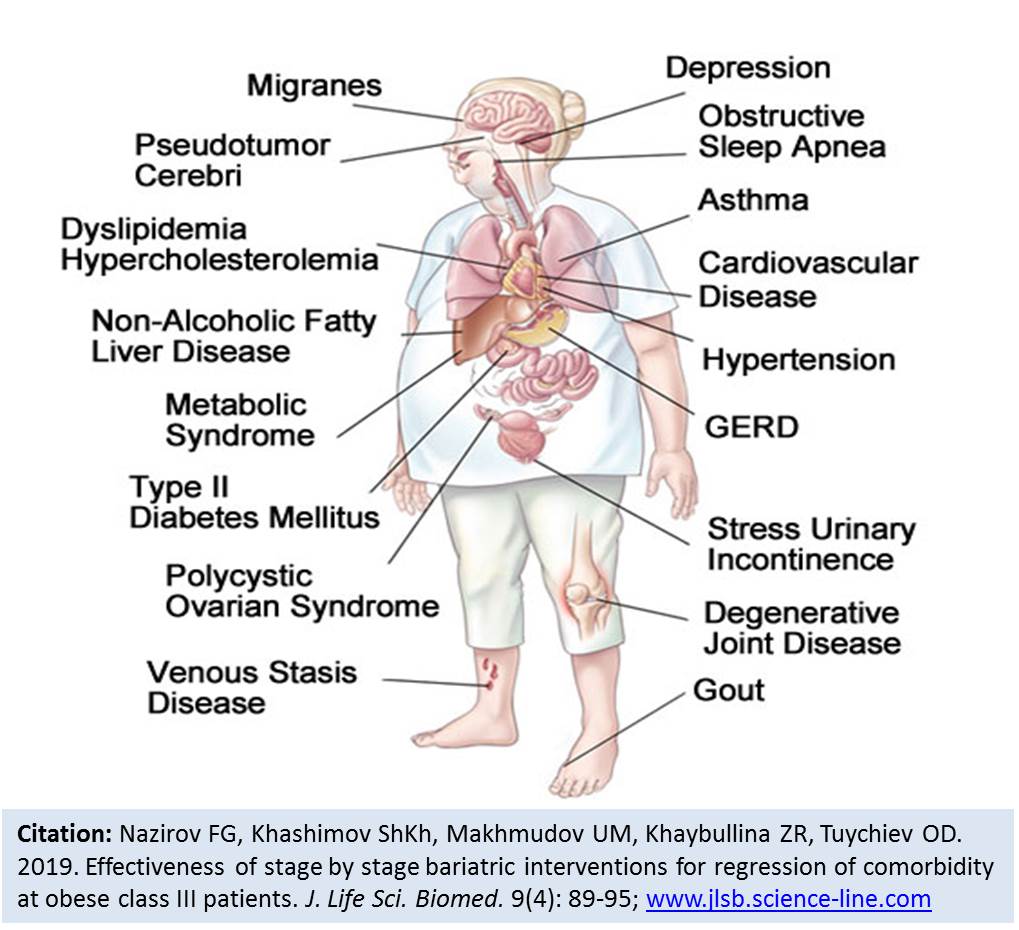
Effectiveness of stage by stage bariatric interventions for regression of comorbidity at obese class III patients.
Nazirov FG, Khashimov ShKh, Makhmudov UM, Khaybullina ZR, Tuychiev OD.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(4): 89-95, 2019; pii:S225199391900014-9
Abstract
Introduction. Currently obesity is considered as a chronic, relapsing, multifactorial neurobehavioral disease, in which an increase in body fat contributes to the dysfunction of adipose tissue and the biomechanical effect of adipose tissue on surrounding tissue with development of metabolic and psychosocial health effects. It has been proven that bariatric surgery significantly reduces the level of pro-inflammatory senility-associated secretory proteins (SASPs), weight reduction increases telomeres length and declines their oxidative degradation (lowering of oxidative stress in telomeres), miR10a_5p, which is post-regulated with increasing of biological age, decreased after surgery, what suggests that bariatric surgery abated the premature aging phenotype. It is of big interest to evaluate comorbidity conditions in people with obese class III after the intervention of intragastric balloons (IGB) and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG), which are lead to weight loss. Methods. A total of 40 patients (32 female and 8 male aged 19–55 years were considered for the study. Comorbidity was assessed by the structure and severity of diseases associated with obesity according to the recommendations of Nedogoda (2016). Cardiometabolic disease staging scale of Guo (2015) was used to assess the metabolic health. Endovisual surgery-LSG was performed (n=40) on a laparoscopic set and instruments of Karl Storz, GMBH & CoKG (Germany). The spherical intragastric balloon (IGB) was installed according to the manufacturer's method (BIB ™ System Intragastric Balloon from Allergan Inc. USA) using a GIF-1T20 Olympus gastrointestinal fibroscope (Japan). Results. Evaluation of the obesity phenotype, a completely metabolically healthy phenotype was not detected in any case. Nowadays, the opinion about the usefulness of the clinical concept of the metabolic syndrome (MS) is disputed, because it has not been convincingly proven its predictive value exceeds that for individual components. Conclusion. Obese class III is associated with dyslipidemia/hypertriglyceridemia in 85%; with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2)/prediabetes in 50%; with arterial hypertension (AH) in 45%; and with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in 35% of cases. Therefore, two-stage treatment by IGB and LSG make it possible to improve the performance on the Cardiometabolic disease staging scale, achieving zero cardiometabolic risk in 35% of patients, and in rest of patients move to a lower stage.
Keywords: Obesity, Bariatric surgery, Comorbidity, Intragastric balloon, Endovisual surgery.
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
Characteristics and early clinical outcomes of patients undergoing living-related kidney transplantation.
Nazirov FG, Bakhritdinov FSh, Ibadov RA, Matkarimov ZT, Suyumov AS, Sobirov JG, Ibragimov SKh.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(4): 96-101, 2019; pii:S225199391900015-9
Abstract
Aim. This study aimed to access early outcomes of living-related kidney transplantation. Methods. The results of treatment of 159 patients (135 males and 24 females) with chronic renal disease during 2010- 2018, have been investigated. Two new and traditional methods have been studied. New optimized method was performed for the main group (n=98) observed since February 2018, while the comparison group (n=61) from 2010 to February 2018 was operated in the traditional way. The characteristics of the patients were compared using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test or the Fisher’s exact test as appropriate. All tests were two-sided, and P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Analyses were performed using the R statistical package. Results. In 149 (93.7%) cases, the functional activity of the kidney transplants was assessed as a primary functioning graft with 95 (96.9%) cases in the main group and 54 (88.5%) in comparison group (P=0.048). Delayed graft function was detected in 2 (2.0%) recipients of the main group and in 5 (8.2%) cases of the comparison group. In the postoperative period, a significant decrease in creatinine level was observed in the main group of recipients and on the 1st day it was 221.0±58.7μmol/L, whereas in the comparison group the index was 569.3±84.6 μmol/L (P<0.001). 3-4 days after surgery, the level of blood creatinine in the main group was significantly (P<0.01) lower than the comparison group (149.6±25.6 vs. 343.6±69.4 μmol/L). On the first day after surgery, there was also a significant decrease (P<0.05) in urea level of the main group (11.4±1.61 mmol/L) in comparison with the comparative group (15.4±0.84 mmol/L). At the time of hospital discharge of recipients, the level of urea was within normal limits and equal to 8.3±0.80 mmol/L and 9.0±0.95 mmol/L in the main and comparison groups, respectively (P>0.05). Hemodialysis was required in 3 (3.1%) recipients from the main group and 3 (4.9%) from the comparison group. The need for corticosteroid therapy was observed in 2 (2.0%) cases of the main group and in 3 (4.9%) cases from the comparison group. Conclusion. The effectiveness of improved approaches to patient management and surgical tactics of related kidney transplantation has been proved, taking into account the verification of the graft functional activity on the main clinical and biochemical data of the terminal stage of chronic renal failure regression.
Keywords: Kidney Transplantation, Living-Related Renal Transplant Recipients, Early Clinical Outcomes
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
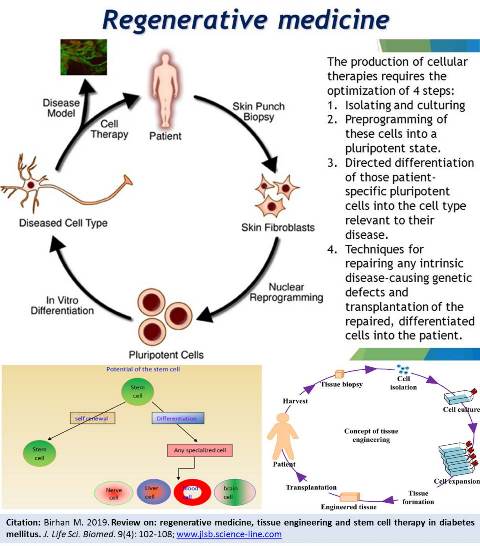
Review on: regenerative medicine, tissue engineering and stem cell therapy in diabetes mellitus.
Birhan M.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(4): 102-108, 2019; pii:S225199391900016-9
Abstract
Introduction. In view of the recent success in pancreatic islet transplantation, interest in treating diabetes by the delivery of insulin-producing β-cells has been renewed. Because differentiated pancreatic β-cells cannot be expanded significantly in vitro, β-cell stem or progenitor cells are seen as a potential source for the preparation of transplantable insulin-producing tissue. In addition to embryonic stem (ES) cells, several potential adult islet/β-cell progenitors, derived from pancreas, liver, and bone marrow, are being studied. To date, none of the candidate cells has been fully characterized or is clinically applicable, but pancreatic physiology makes the existence of one or more types of adult islet stem cells very likely. It also seems possible that pluripotential stem cells, derived from the bone marrow, contribute to adult islet neogenesis. Aim. In future studies, more stringent criteria should be met to clonally define adult islet/β-cell progenitor cells. If this can be achieved, the utilization of these cells for the generation of insulin-producing β-cells in vitro seems to be feasible in the near future. This review will focus on the potential of adult tissue-derived stem cells, in lieu of embryo-derived stem cells, for the treatment of diabetes. We discuss the role of adult islet stem/progenitor cells in normal physiology, highlight possible candidate cells isolated to date, and describe different approaches for stem cell-based therapy.
Keywords: Embryonic Stem Cells, Insulin-Producing, Pancreatic Islet, Physiology, β-cells
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
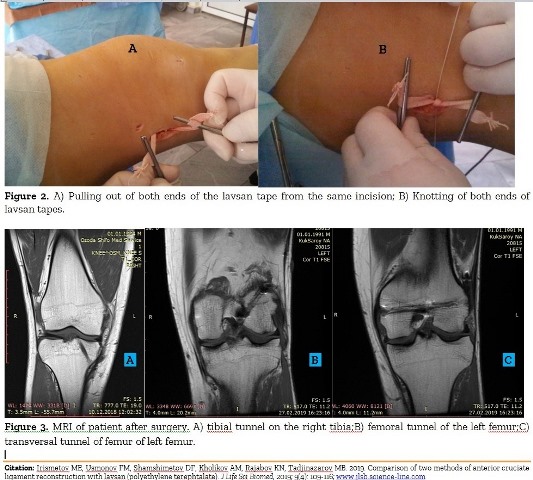
Comparison of two methods of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with lavsan (polyethylene terephtalate).
Irismetov ME, Usmonov FM, Shamshimetov DF, Kholikov AM, Rajabov KN, Tadjinazarov MB.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(4): 109-116, 2019; pii:S225199391900017-9
Abstract
Introduction. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main stabilizateur of the knee joint. Many methods were suggested for its reconstruction with different allo/autografts, as well as synthetic materials. Aim. The study aimed to compare two methods of ACL reconstruction with lavsan (polyethylene terephtalate). Methods. The study included 102 patients who underwent ACL reconstruction with lavsan tape (polyethylene terephtalate). Group 1 (46 patients) underwent single-bundle ACL reconstruction, and group 2 (56 patients) underwent double-bundle reconstruction. Patients were evaluated with Lachman, anterior drawer and pivot-shift tests and Lysholm score. Results. Our results showed better results in double-bundle group, especially rotational stability was significant better. Besides that majority of patients of I group had some problem flexion of the operated knees. Conclusion. Independent of the method of ACL reconstructions these surgeries must be perform taking into account anatomic features and changes of the knee. Double-bundle technique of ACL reconstruction with lavsan provides better stability than single-bundle technique.
Keywords: Anterior Cruciate Ligament, Single-Bundle Technique, Double-Bundle-Technique, Synthetic Material
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
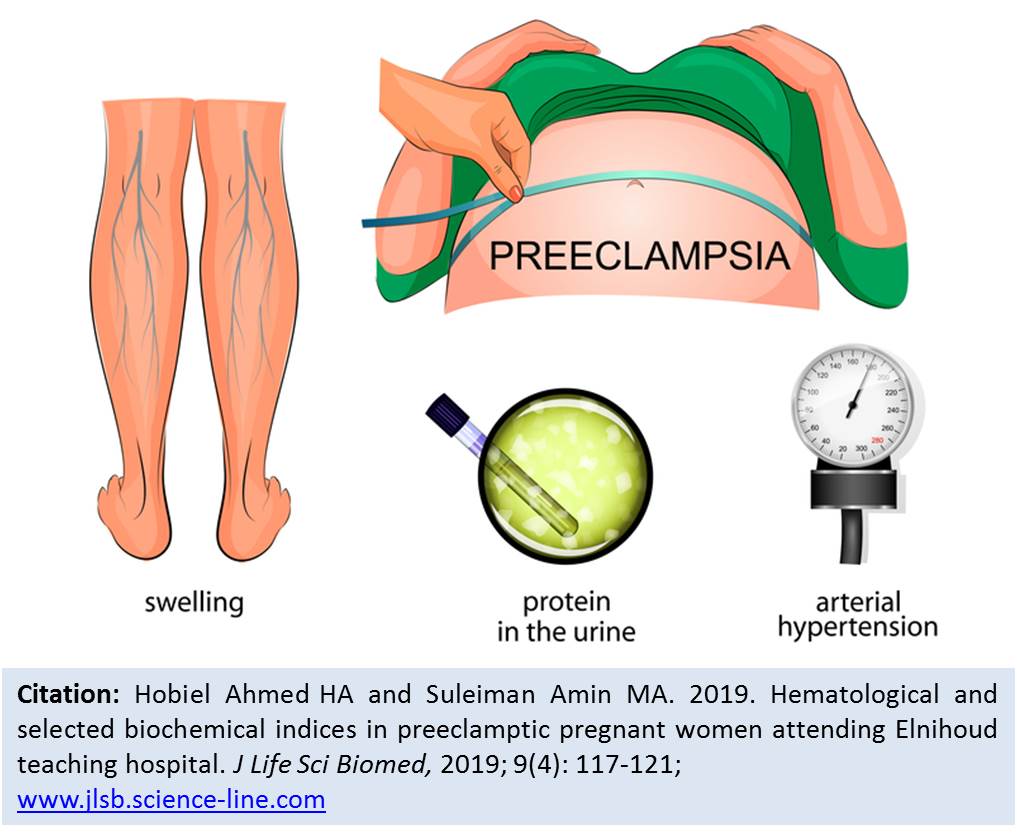
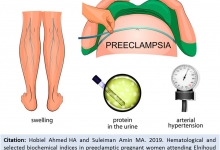
Hematological and selected biochemical indices in preeclamptic pregnant women attending Elnihoud teaching hospital.
Hobiel Ahmed HA and Suleiman Amin MA.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(4): 117-121, 2019; pii:S225199391900018-9
Abstract
Background. Preeclampsia (PE) is a form of hypertensive disorder of pregnancy, leading to maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality worldwide. It is major obstetric problem in developing countries and affecting 2–10% of all pregnancies. Aim. This study aimed to evaluate hematological and some biochemical parameters in preeclamptic pregnant women attending Elnihoud Teaching Hospital, Sudan, and to compare the findings with the severity of the disease. Methods. A descriptive cross sectional study was carried out in Elnihoud Teaching Hospital with total of forty tow pregnant women as participants (14–45 years old). They were selected from the Wards of the Hospital at admission before starting treatment. Hematological and selected biochemical parameters were measured and analyzed for every preeclamptic patient. Results. The study revealed no significant elevation in plasma total protein, total white blood cells (TWBCs), lymphocytes and mean corpuscular volume (MCV) among severe preeclamptic patients versus mild cases. Decrease with no significant value in hemoglobin level, platelets count (PLT), red blood cells (RBCs) and mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) was observed in severe preeclamptic cases compared to mild preeclamptic cases. Conclusion. It is concluded that measurement of hematological and some biochemical parameters might reflect to some extent the effect of preeclampsia on pregnant women. Recommendation. Further studies with more parameters can provide guidance for the evaluation intervention and management of pregnant women who suffering from PE.
Keywords: Preeclampsia, Hypertension, Proteinuria, Papillodema.
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 9 (2); March 25, 2019 [Booklet]![]()
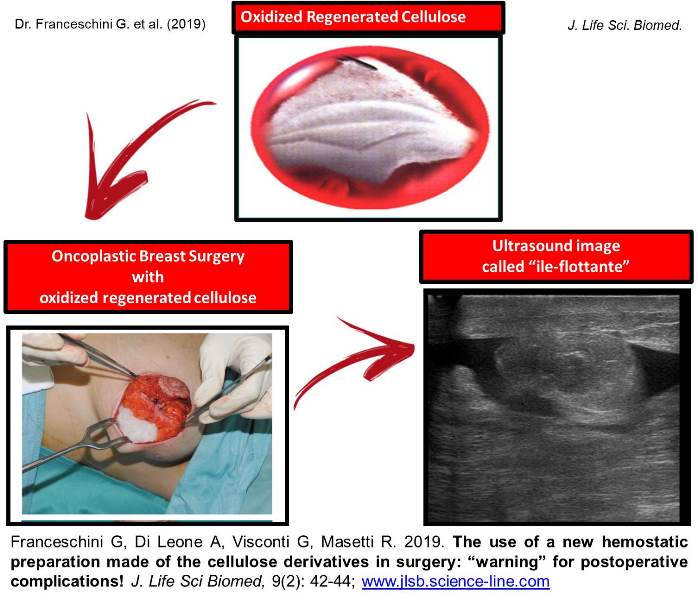
The use of a new hemostatic preparation made of the cellulose derivatives in surgery: “warning” for postoperative complications!
Franceschini G, Di Leone A, Visconti G, Masetti R.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(2): 42-44, 2019; pii:S225199391900007-9
ABSTRACT
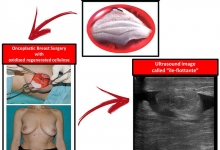
Introduction. We have read with interest the article by Rustam Abrarovich Sadykov et al. (2019) on “New hemostatic preparation made of the cellulose derivatives”. The Authors present their early experience on new samples of pellicle hemostatic coverage on the basis of the cellulose derivatives. They conclude: “Rapid enough biodegradation of polymer along with the unexpressed inflammatory reaction allows preventing the infecting related to the presence of foreign body. The rapid forming of fibrotic tissue in a zone of lesion makes it possible to obtain a durable hemostasis”. Results. In our series we noted a 10% rate of allergic skin reactions with irritation, redness, itching, swelling, rash and hives in the mammary region, successfully managed with steroids and antihistamine medications. In addition, we experienced a significant seroma in the site of oxidized regenerated cellulose (ORC) placement in 45% of our patients. Conclusion and Recommendation. When using a new preparation made of the cellulose derivatives, as a possible aid to reduce the risk of postoperative haematoma and infections it is important to discuss with the patient also about possible postoperative complications. It is also important that surgeons specify clearly the use of this biomaterial in the report of the surgical procedure so that radiologists can properly interpret the sonographic findings due to this biomaterial and avoid misdiagnosis and undue alarmism during the follow-up of these patients.
Keywords: Hemostasis, Oxidized Cellulose, Polymer
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
Geprotsel, biocompatible implant: comparative estimation of its application results for providing airstasis and hemostasis in the lung surgery.
Khudaybergenov ShN, Eshonkhodjaev OD, and Khalmuratova MK.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(2): 45-51, 2019; pii:S225199391900008-9
ABSTRACT
Introduction. In surgery, the prevention of postoperative complications has always been and remains relevant. One of the most important components that contribute to reducing the number of complications, in addition to effective drainage, restoration of muscle tone and adequate breathing, is reliable aerostasis and hemostasis. When performing operations on the lungs against the background of the presence in patients of factors affecting the incidence of failure in aero- and hemostasis (COPD, emphysema), the risk of developing these complications can reach 11.8% after lobectomy, after wedge-shaped resections up to 9.1% and after decortication up to 33.3%, which is 14.7% for all operations in general (violation of aerostasis - 5.9% and hemostasis - 8.8%. Aim. The aim of study was to investigate the effectiveness of the proposed domestic implant “Geprocel” in the treatment and prevention of disorders of aero- and hemostasis during pulmonary operations. Methods. The study included 69 patients operated in the department of surgery of the Lung and Mediastinum of the "Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Surgery named after Academician V. Vakhidov" State Institution for the period from 2015 to June 2018. Hemostatic implant in the form of a fine powder was developed at RSRCS named after acad. V. Vakhidov”. Geprotsel consists of the following components: the sodium salt of carboxymethyl cellulose, oxidized cellulose and nanocellulose associated with calcium ions (Patent No. IAP 20160273), in accordance with requirements of ISO 10993-1-2011. Results. The use of the Heprotsel biological implant reduced the need for additional single lung tissue flashing to ensure adequate aero- and hemostasis from 38.2% to 11.4% and multiple reinforcement with sutures from 29.4% to 5.7% (χ2 = 7.706; Df = 2; P = 0.021).
Keywords: Aerostasis, Hemostasis, Collagen, Oxidized cellulose, Biodegradable implant, Geprotsel, Heprocel, Pulmonary operations
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
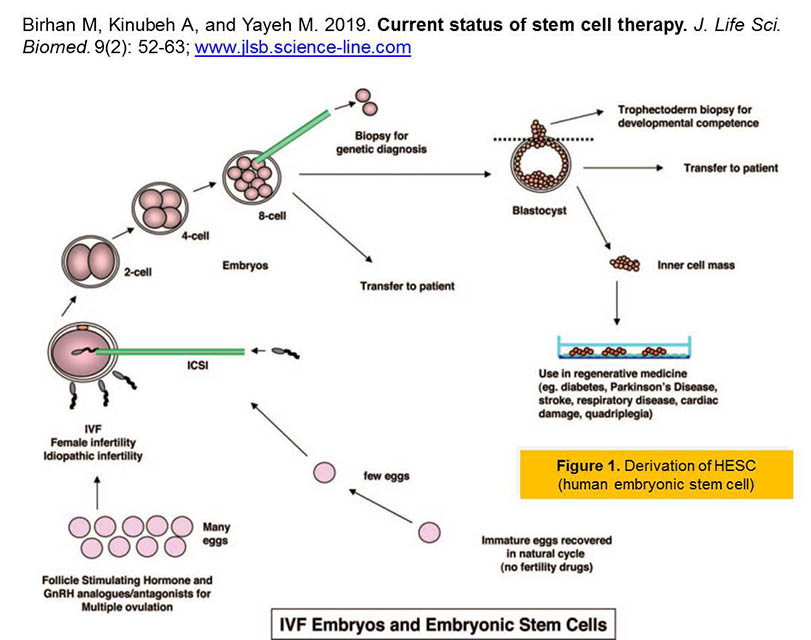
Current status of stem cell therapy.
Birhan M, Kinubeh A, and Yayeh M.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(2): 52-63, 2019; pii:S225199391900009-9
ABSTRACT
Introduction. Stem cells have the extraordinary potential to develop into many diverse cell types in the body during early life and growth. Significant progress has been made in understanding the biochemical and metabolic mechanisms and feedback associated with different stem cells response. Some of the challenges concerning transplanted embryonic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells are immune-mediated rejection, senescence-induced genetic instability or loss of function, and limited cell survival. Aim. The aim of this review, is to recapitulate the recent status and information about the use of embryonic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells for research into how cells and tissues of the body grow and develop, and potentially useful for curing disease. Results. Stem cell therapy efforts are currently underway for virtually every type of tissue and organ within the human body. Because the current status of stem cell incorporates the fields of cell transplantation, materials science, and engineering, personnel who have mastered the techniques of cell harvest, culture, expansion, transplantation, and polymer design are essential for the successful application of this technology. Various stem cell therapies are at different stages of development, with some already being used clinically, a few in preclinical trials, and some in the discovery stage. Recommendations. Recent progresses suggest that stem cell therapy may have expanded clinical applicability in the future because they represent a viable therapeutic option for those who require tissue and cells replacement in diverse degenerative disease. More recently, major advances in the areas of stem cell biology, tissue engineering, and nuclear transfer techniques have made it possible to combine these technologies to create the comprehensive scientific field of regenerative medicine. “But there is a strong need for better understanding the biology, manipulation and safety of stem cells in tissue regeneration and repair before starting the therapeutic applications.”
Keywords: Embryonic Stem Cell, Mesenchymal Stem Cell, Regenerative
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 9 (3); May 10, 2019 [Booklet]![]()
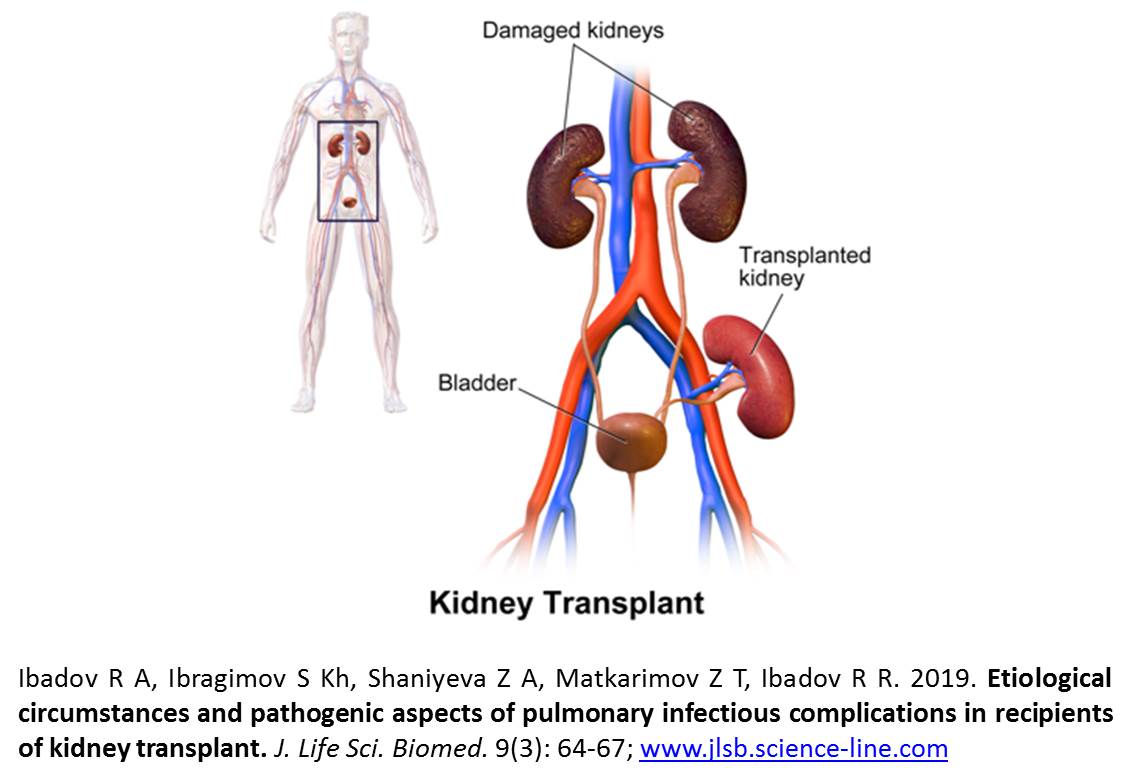
Etiological circumstances and pathogenic aspects of pulmonary infectious complications in recipients of kidney transplant.
Ibadov R A, Ibragimov S Kh, Shaniyeva Z A, Matkarimov Z T, Ibadov R R.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(3): 64-67, 2019; pii:S225199391900010-9
Abstract
Aim. This study aimed to determine the spectrum of pathogens and its resistance in the dynamics in patients with infectious complications after kidney transplantation. Methods. The results of the study of biomaterials from patients with infectious complications on the background of acute and chronic kidney transplant rejection have been studied. Results. During the analyzed period, there was a tendency to change the spectrum of pathogens, the growth of the value of gram-negative bacteria. The sensitivity analysis of the isolated microorganisms over the study period (2010-2017) showed an increase in the resistance of the dominant pathogens. Also, there was a significant increase in the frequency of occurrence of Candida fungi. Conclusion. In most kidney transplant recipients with nosocomial infections is unavoidable. Therefore, a timely and adequate antibiotic therapy is required to constant control of modern pathogens with increased resistance. Recommendations. The increase in antibiotic resistance of the leading pathogens makes it necessary to study the antibioticogram of all strains isolated from patients for an adequate choice of effective antibiotic therapy. The obtained data should be used to optimize empirical antibiotic therapy in patients with purulent-septic complications after kidney transplantation.
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Immunosuppression, Chronic graft rejection, Infection, Lung damage, Intensive care
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
Review on: biodiversity, ecosystem services and genetically modified organisms.
Birhan M, Dejene H and Kenubih A.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(3): 68-73, 2019; pii:S225199391900011-9
Abstract
Introduction. Understanding the relationship between ecosystem and diversity requires knowledge of how species interact with each other and how each is affected by the environment. It is useful to distinguish between the instantaneous effects of species richness on ecosystems and those which become deceptive on a longer time scale, described here as filter and founder effects. Biological diversity appears to enhance the resilience of desirable ecosystem states, which is required to secure the production of essential ecosystem services. Aim. The diversity of responses to environmental change among species contributing to the same ecosystem function, which we call response diversity, is critical to resilience. Response diversity is particularly important for ecosystem renewal and reorganization following change. Here we criticism the various roles that biodiversity, ecosystem services and genetically modified organisms play in terrestrial ecosystems with special emphasis on their contribution to productivity and diversity. Therefore, the aim of this review is summarizing of different articles and writing of the effects of one to the others, and the relation between biodiversity, ecosystem services and genetically modified organisms.
Keywords: Biodiversity, Ecosystem services, Genetically modified organisms
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
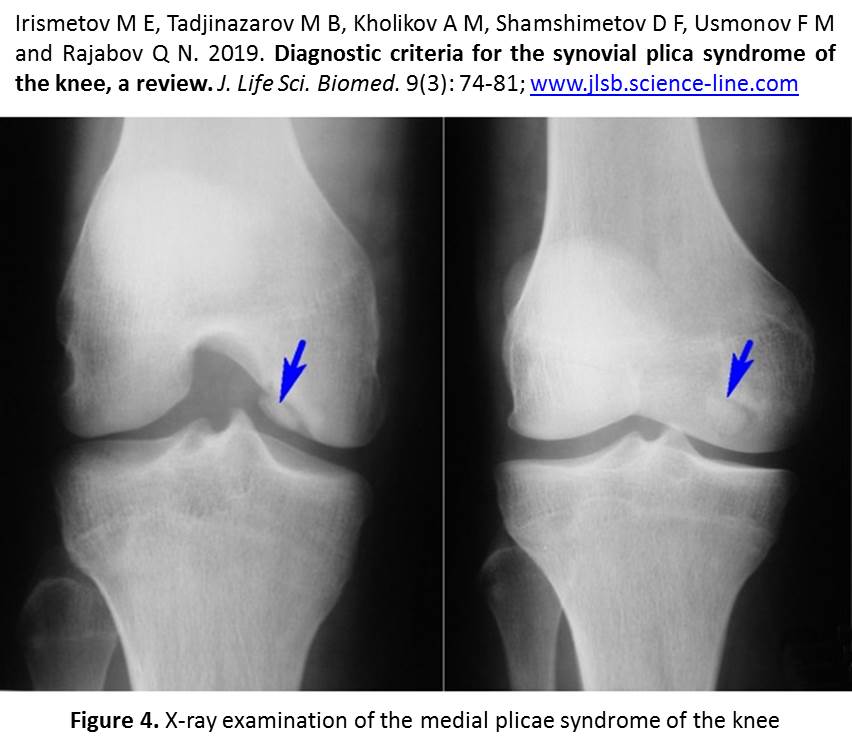
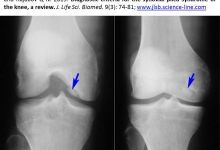
Diagnostic criteria for the synovial plica syndrome of the knee, a review.
Irismetov M E, Tadjinazarov M B, Kholikov A M, Shamshimetov D F, Usmonov F M and Rajabov Q N.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(3): 74-81, 2019; pii:S225199391900012-9
Abstract
Aim. Based on literature review, the article highlights the current diagnostic criteria for the synovial plicae syndrome (SPS) of the knee. Introduction. The syndrome diagnosis algorithm includes a carefully collected clinical history and clinical examination using specific functional tests, non-invasive research methods (ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging) and arthroscopy. Discussion. It should be noted that the principles of early diagnosis by clinical and radiological methods are still not well understood. Due to non-specific clinical symptoms, this syndrome in most cases is detected by arthroscopic intervention. Conclusion. We try to provide an evidence-based guide to the diagnosis criteria of the knee SPS, based on the analysis of the literature and our own experience.
Keywords: Knee joint, Pain syndrome of the knee, Synovial plicae syndrome, Diagnostic
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 9 (1); January 25, 2019 [Booklet]![]()
 Research Paper
Research Paper
Features of the psychoemotional condition of women with induced pregnancy.
Asatova MM, Saidazova ShSh, and Voitova GA.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(1): 01-04, 2019; pii:S225199391900001-9
Abstract
The objective of the present study was to evaluate special features of the psychological health of women with induced pregnancy and its relationship with nausea and vomiting. The Spielberger scale score results of 270 women with nausea and vomiting during of induced-pregnancy (NVIP) has been studied. The mean age of the women was 25±4.2 years. Results showed that, 31 (11,5%), 118 (43.7%) and 121 (44.8%) of pregnant women with NVIP had low, moderate and high degree of anxiety, respectively. Most of the surveyed women with NVIP (72.2%) experienced a high level of situational anxiety. For moderate and low degrees of state anxiety, the approximately equal frequency was registered, 14.1% (n=38) and 13.7% (n = 37), respectively. The state of tension and regretful from the current situation was noted by 175 (64.8%), anxiety and nervousness were registered in 158 (58.5%) and 207 (76.7%) cases, respectively. 147 (54.4%) and 187 (69.3%) women, respectively, noted their excitement for possible failures and concern. 72.2% of women with induced pregnancy have state anxiety as a result of the emotional reaction to NVIP, which indicates the need for counseling by psychologists.
Keywords: Induced pregnancy, First trimester, Nausea and vomiting, Trait and state anxiety, Spielberger scale
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]

Research Paper
Impact of school meals’ type and time on children's food consumption, physical and behavioral activities.
Yousefi M and Yousefi Z.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(1): 05-09, 2019; pii:S225199391900002-9
Abstract
Today, proper nutrition is one of the useful tools for the healthiness and sustainability of people's diet and especially student performance and behavior in school. Existing nutrient standards for school meals are always important when packed foods or lunches brought from home. The aim of the present study was to determine the effects of school meals type and time on behavioral response, physical activity and the body mass index (BMI) in elementary students of Razan city, Iran. Elementary school principals (N = 16) and total of 234 students selected from 5 schools completed a survey on the school food and physical and behavioral activitıes environment. Students were weighed and measured for their body mass index (BMI) that calculated using a standard protocol and also send a BMI report card to their parents. Results of this study showed that effect of type of time regulation in school nutritional program could significantly improve behavioral response, and especially physical activity and BMI and it can be considered as an applicable strategy to the implementation of such programs on the health status of students.
Keywords: Elementary students, Body mass index, Nutritional behavior, Physical activity
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
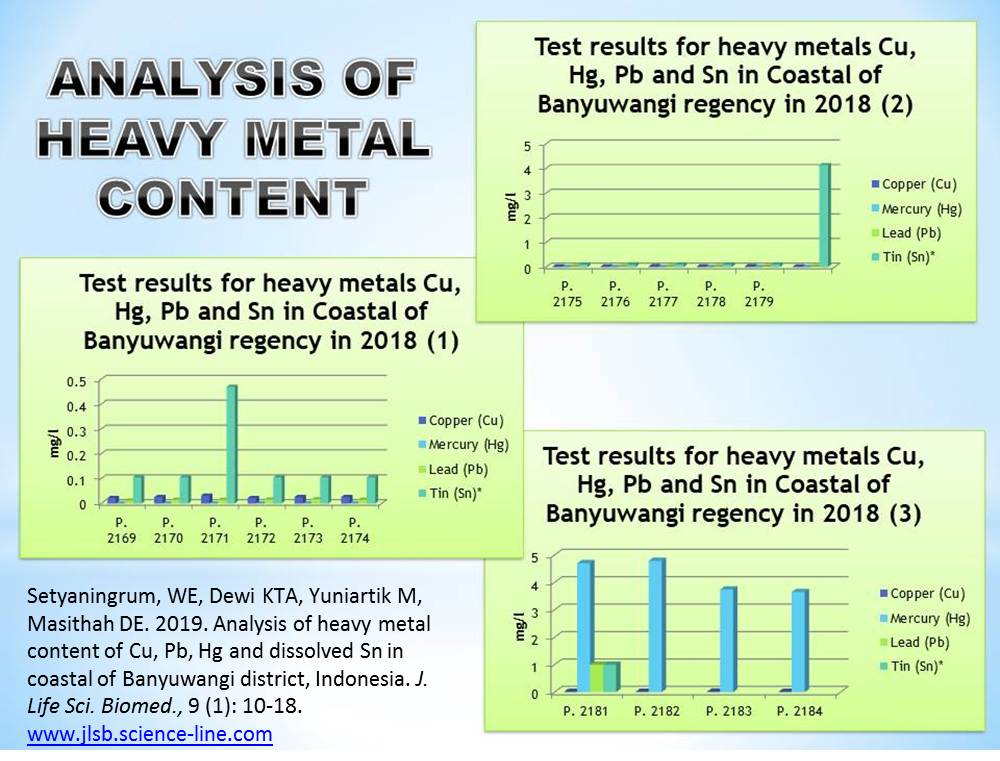
Analysis of heavy metal content of Cu, Pb, Hg and dissolved Sn in coastal of Banyuwangi district, Indonesia.
Setyaningrum, WE, Dewi KTA, Yuniartik M, Masithah DE.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(1): 10-18, 2019; pii:S225199391900003-9
Abstract
Banyuwangi Regency has the longest coast in East Java of Indonesia with sandy beaches and corals and there are various types of coastal and marine resources that can be utilized both in terms of economics and environment. But in the current era of industrialization, coastal areas in Banyuwangi have become a top priority for industrial development, agribusiness, agro-industry, housing, transportation, ports and tourism. The purpose of this study was to analyze the content of copper (Cu), lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), and tin (Sn) and the effect of water quality on the heavy metal content in the coast of Banyuwangi Regency. The method in this study uses descriptive. Data taken along the coast of Banyuwangi Regency include water quality (alkalinity, NH4, PO4, DO, pH, NO3, water temperature and salinity), copper (Cu), lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), and tin (Sn). Data analysis using multiple linear regression analysis, followed by F test and t-test. The results showed that there was an influence between the quality of the water on the value of heavy metal of copper (Cu), and the value of R-Square 0.681 which means that it has an influence proportion on the value of copper (Cu) of 68.1%. Likewise, for the quality of water for tin (Sn), there is an influence with the value of R-Square of 0.700, which means that the effect is as high as 70%. While the quality of the waters against Lead, heavy metal (Pb) and mercury (Hg) has no significant effect. Based on the results of the study, Banyuwangi district government needs to take serious actions in controlling heavy metal pollution through the implementation of law No. 23 of 1997 concerning to environmental management, and the application of environmental quality standards more strictly.
Keywords: Banyuwangi coastal, Copper (Cu), Heavy metals, Lead (Pb), Mercury (Hg), Tin (Sn), Water quality
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
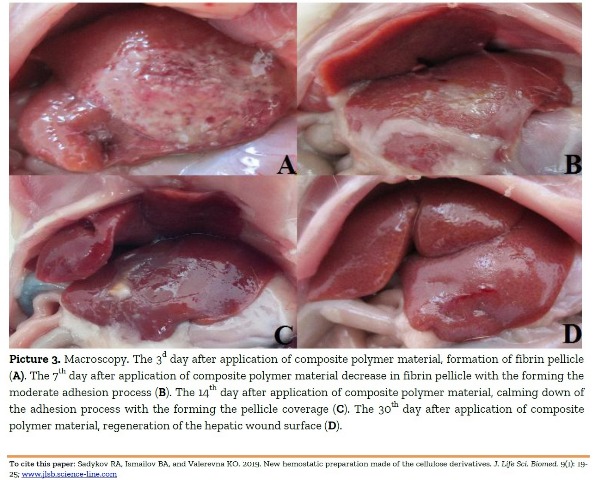
New hemostatic preparation made of the cellulose derivatives.
Sadykov RA, Ismailov BA, and Valerevna KO.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(1): 19-25, 2019; pii:S225199391900004-9
Abstract
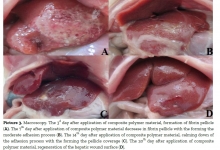
Aim. The aim of this study was to investigate the indexes the indexes of biocompatible pellicle hemostatic coverage in vitro and in vivo conditions. Methods. Samples of pellicle hemostatic coverage on the basis of the cellulose derivatives were used in researches. Breaking strength, estimation of the implant’s structure and adhesion power were evaluated according to the Ts 05957837-28:2014 instructions and documents of the National certification system of the Republic of Uzbekistan and with the using the apparatus "Zwick" (Germany) and atomic-power microscope of Agilent technologies (USA). Hemostatic activity of the coverage on the basis of the cellulose derivatives was estimated by the Lee and White test for the blood coagulation time. For in vivo research, 30 mature rats were required. Operations were performed under inhalation anesthesia, and the wound of liver was formed. Both macroscopic and microscopic studies had been undertaken. Morphological changes were studied in terms of 3 and 12 hours and then on the 1st, 3d, 7th, 14th and 30th day after an operation. Results. An adhesion power of the pellicle coverage on the basis of the cellulose derivatives was 7.3± 0.2 N/cm2, breaking strength was 390±4.8 kGf/cm². In presence of polymer, a coagulation time on Lee and White test was shortened by as many as 2.1 times in relation to control that made up 2.4± 0.6 min. In in vivo conditions hemostasis started during 3-5 sec. A weak inflammatory reaction of tissue was histologically determined. Further observations over dogs showed that an hour after an operation, an implant had been preserved on the surface of liver as a white pellicle and had not been separated from the wound surface. Bleeding signs were not marked. An abdominal cavity remained intact. Conclusion. Rapid enough biodegradation of polymer along with the unexpressed inflammatory reaction allows preventing the infecting related to the presence of foreign body. The rapid forming of fibrotic tissue in a zone of lesion makes it possible to obtain a durable hemostasis. A poorly expressed reaction was also marked from the side of peritoneum and surrounding organs. Recommendations. The oxidized regenerated cellulose can result in an intensive inflammation of the surrounding tissues because of the low level of pH that had not happened in the present research due to the selected correlation of ingredients of hemostatic pellicle.
Keywords: Hemostasis, Morphology, Carboxymethylcellulose, Oxidized Cellulose, Hemostatic Substance.
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
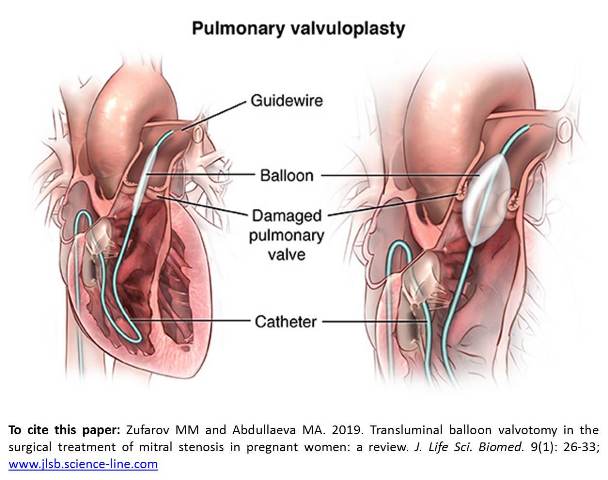
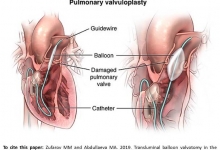
Transluminal balloon valvotomy in the surgical treatment of mitral stenosis in pregnant women: a review.
Zufarov MM and Abdullaeva MA.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(1): 26-33, 2019; pii:S225199391900005-9
Abstract
Aim. The aim of this study was to investigate current strategies in treatment of pregnant women suffering with mitral stenosis. Mitral stenosis is an obstruction of the pathway of the left ventricle flow at the mitral valve (MV) level as a result of the structural deformation of the MV apparatus, which prevents the necessary opening of the MV during the diastolic filling of the left ventricle. The most frequent lesion of valves in women with rheumatic heart disease (RHD) is MV. It remains the most common acquired valvular lesion in pregnant women and is one of the main causes of maternal death from cardiovascular diseases. According to the literature mitral stenosis (MS) is found in 75–90% of pregnant women with acquired heart defects. In addition, the incidence of fetal morbidity is positively correlated with the severity of MS: it increases from 14% in pregnant women with mild MS to 28% in people with moderate MS and 33% in women with severe mitral stenosis. The course of MS in pregnant women depends on the clinical manifestations, the degree of severity of heart failure, and the degree of rheumatic fever activity. Conclusion. The advantages of minimally invasive techniques during pregnancy are theoretically undeniable. The choice of the optimal method of delivery, the assessment of the fetal state of the fetus and the methods for its correction are also fundamental.
Keywords: Mitral stenosis, Left ventricle, Pregnancy, Women
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
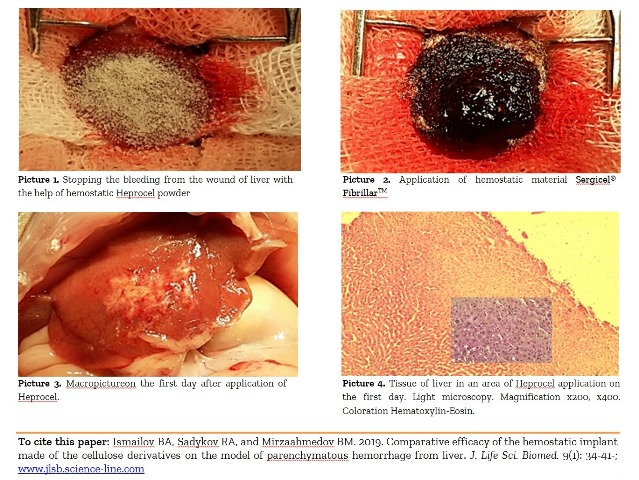
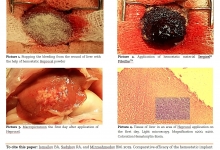
Comparative efficacy of the hemostatic implant made of the cellulose derivatives on the model of parenchymatous hemorrhage from liver.
Ismailov BA, Sadykov RA, and Mirzaahmedov BM.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(1): 34-41, 2019; pii:S225199391900006-9
Abstract
Aim. The aim was to study the comparative efficiency of the hemostatic implant made of the cellulose derivatives on a model of the parenchymatous hemorrhage from a liver. Methods. Experimental studies on the biocompatibility’s evaluation were conducted in accordance with the Russian national standard ISO 10993-6-2011. Operations have been performed under the general anaesthetizing with the modeling the parenchymatous hemorrhage from the wound of liver. A total of 72 white mature outbred rats of both sexes weighing 196.5±2.8 g were used from which 36 ones made up group of comparison using the application hemostatic material, Sergicel® FibrillarTM. In the basic group of rodents (36) powder Heprocel in equal amounts by weight of 30 mg was applied on a wound. Results. From the results it is possible to come to a conclusion that the hemostatic Heprocel implant causes on the first day morphological reaction of liver as an inflammation and a spread of the connecting tissue, but these processes calm down quickly. An inflammatory reaction was less expressed than the control group. To the 30th day in the basic group after application of Heprocel biodecomposition of hemostatic implant was being marked, there were regenerator processes in the liver’s parenchima especially in the zone of lesion that testifies to renewal of liver’s tissue, while in a comparison group an active degradation of the application hemostatic material began on the 30th day and an expressed adhesion process in an abdominal cavity took place. Conclusion. Hemostatic powder closely adjoins the liver’s tissue, stops bleeding, cases of relapse of bleeding were not marked. Histological researches conducted in the dynamics of the healing showed that the wounds of liver educed that Heprocel did not cause the expressed inflammatory reaction, the zone of lesion did not exceed 150 µm, and the biodecomposition started after 14 days.
Keywords: Hemostasis, Parenchymatous Hemorrhage, Liver, Cellulose’s derivatives, Experimental surgery, Hemostatic implant, Morphology of liver.
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]





-2.jpg)